

However, stating a new name for the keys saves them to different files. Generating new keys overwrites the current ones by default. If there are keys already, the output shows the directory contents: Check for existing keys with: ls -l ~/.ssh/id* How to Generate & Set Up SSH Keys on CentOS 7.Ģ.How to Generate & Set Up SSH Keys on Debian 10.How to Generate SSH Keys on Ubuntu 18.04.Note: For a more detailed OS-specific tutorials, check out our in-depth guides: The basic instructions for Linux, macOS, and Windows are outlined below. Generate the SSH key pair on the local server using OpenSSH. For automation purposes, key management software and practices apply since the private key stays unprotected otherwise. Adding a passphrase to encrypt the private key adds a layer of security good enough for most user-based cases. The model assumes the private key is secured.

The server allows access to anyone who proves the ownership of the corresponding private key. The server stores and marks the public key as approved.Ĥ. Add the corresponding public key to the server.ģ. The private key stays on the local machine.Ģ.
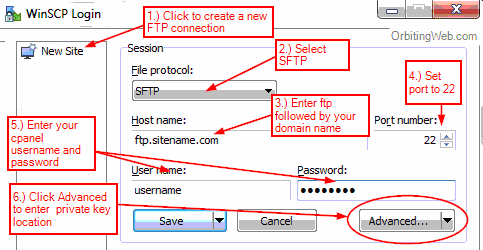
Generate a private and public key, known as the key pair. The SSH public key authentication has four steps:ġ. Follow our guides to turn on SSH on Linux: Ubuntu 18.04, Debian 9 or 10.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
